Duplex Communication
Duplex communication is a method of communication where information can be transmitted and received simultaneously in both directions. This means that two devices can send and receive data at the same time, allowing for real-time communication between them.
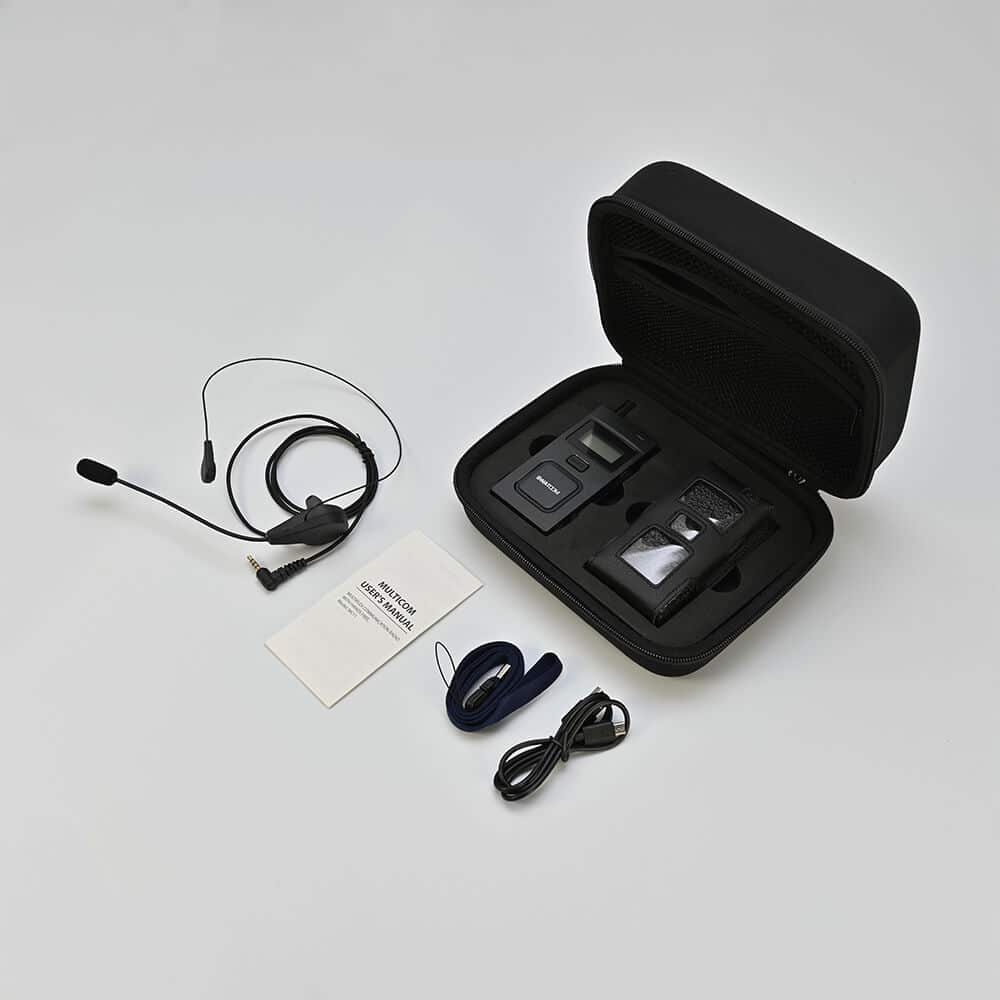
SWATCOM Multicom1
0-5 Users
- Up to 5 users in full duplex
- Headset options
- 400 meters line of sight
- 10 hrs rechargeable battery life
- 40 channels available
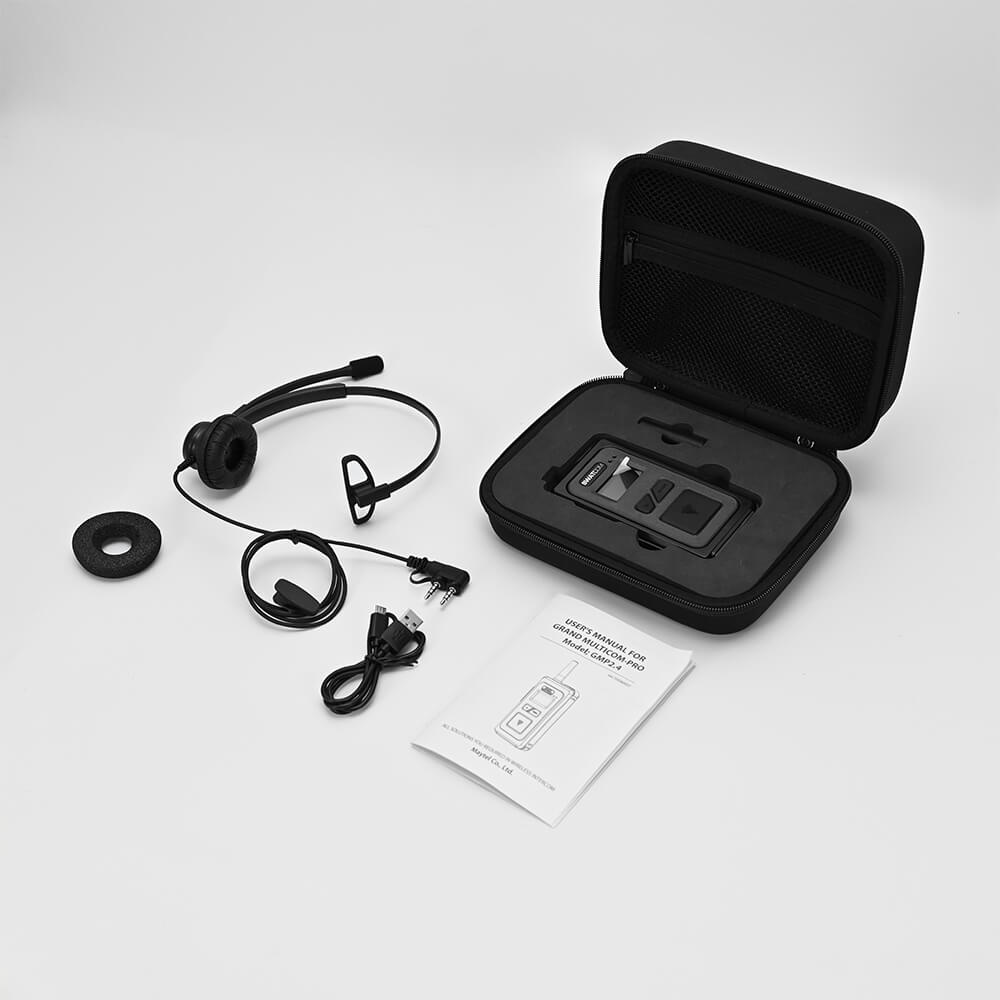
SWATCOM Multicom2
0-10 Users
- Up to 10 users in hands free (full duplex)
- Talk range 400m
- Secure PIN encryption
- License free
- Up to 90 listen only users
SWATCOM Multicom3
0-10 Users
- Up to 10 users in hands free (full duplex)
- Talk range 400m
- Clips onto safety helmets
- License free
- Up to 90 listen only users
Places where full duplex communication is used
What’s the difference between half-duplex and full-duplex?
Full-duplex means that speech can be simultaneously transmitted & received (As you would on talking a phone call).
Half-duplex requires transmission to communicate (Push-to-talk switch).
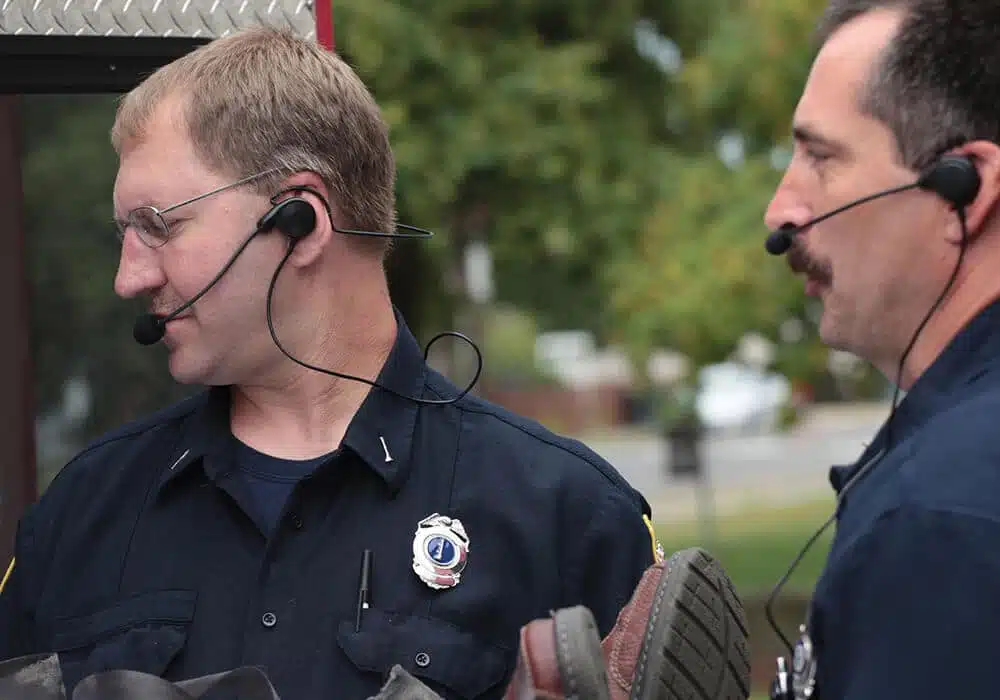
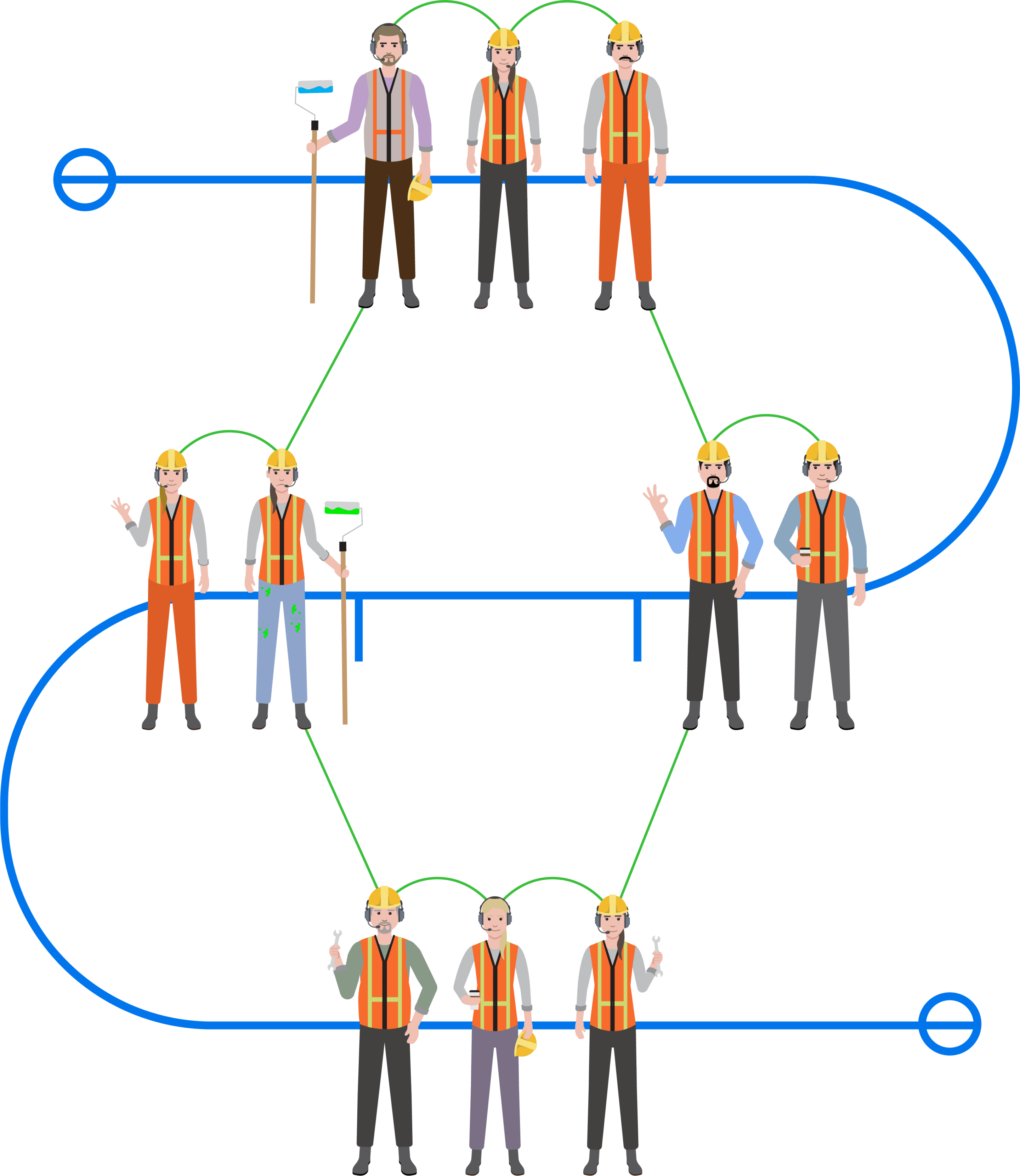
Team communications for professionals.
SWATCOM provide duplex communications into a wide range of environments around the world, supporting professionals in some of the most demanding environments.
Our duplex team communications will allow up to 10 users to communicate simultaneously as if you would talking on a phone call (In full-duplex).
This enables a team to remain in natural free flowing communication, offering the ability to increase safety & efficiency with real time communication between workers.
What is Half-Duplex?
Half-duplex communication is a communication method where information can be transmitted in both directions, but only in one direction at a time. This means that the communication channel can either transmit or receive information, but not both simultaneously.
In other words, when one device is transmitting data, the other device can only receive data, and vice versa. This is in contrast to full-duplex communication, where both devices can transmit and receive data simultaneously.
Examples of half-duplex communication include two-way radio, walkie-talkies and CB radios, where only one person can talk at a time and the other person must wait until the first person has finished speaking before they can transmit their own message. Another example is the Ethernet bus topology, where nodes can send and receive data, but only one node can send data at a time.





